how to test accessory nerve

The accessory nerve is a crucial component of the nervous system that plays a vital role in controlling the movement of certain muscles in the head and neck. Testing the functionality of this nerve is essential in diagnosing various neurological conditions and determining the best course of treatment. In this article, we will explore the process of testing the accessory nerve, understanding its anatomy and function, preparing for the test, conducting the test, interpreting the results, and the post-test care. Let’s delve into the details.
Understanding the Accessory Nerve
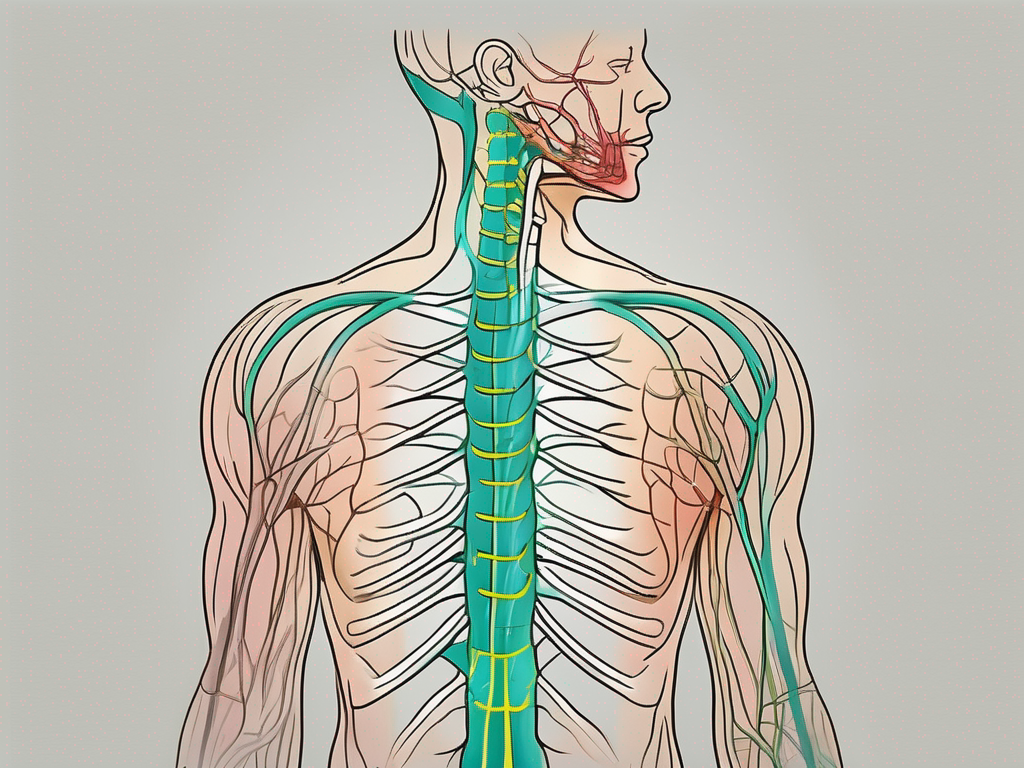
The accessory nerve, also known as Cranial Nerve XI, is a motor nerve that is primarily responsible for controlling the voluntary movements of certain muscles in the head and neck region. It consists of two branches – the cranial part and the spinal part. The cranial part arises from the brainstem, while the spinal part originates from the upper spinal cord.
The accessory nerve is a fascinating component of the human nervous system. Its intricate network of fibers and connections allows for precise control and coordination of various muscles involved in head and neck movements. Let’s delve deeper into the anatomy and function of this remarkable nerve.
Anatomy of the Accessory Nerve
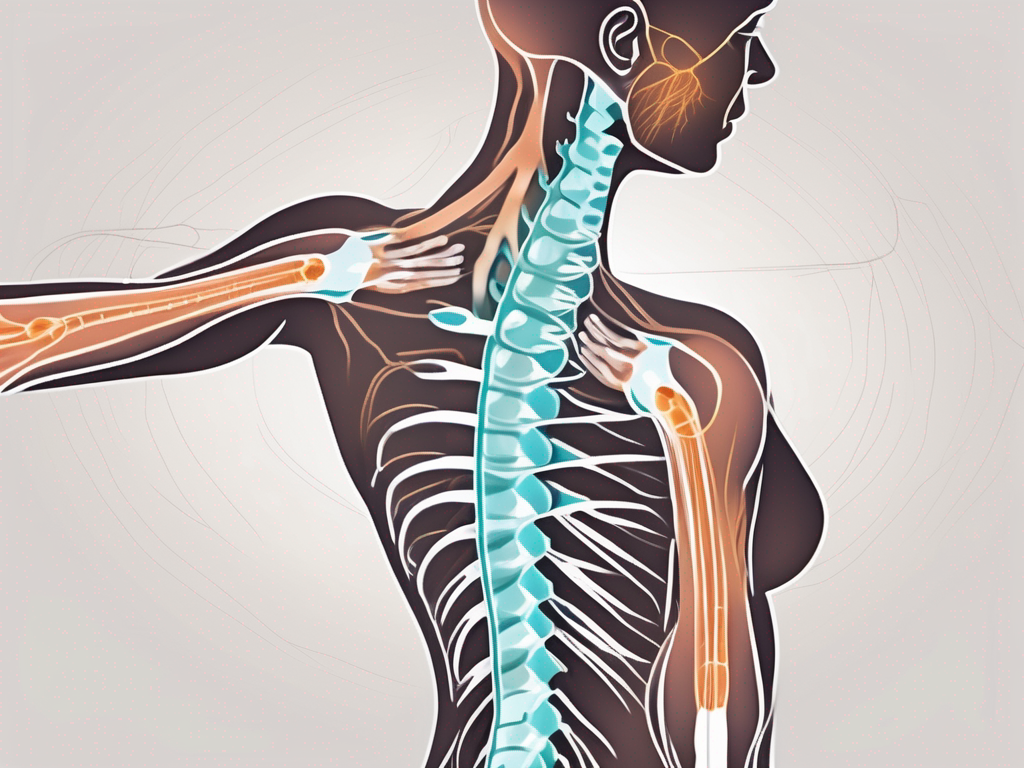
The accessory nerve travels through the skull and neck, passing through several muscles and structures along the way. It innervates the sternocleidomastoid muscle, which helps with head rotation and neck flexion, as well as the trapezius muscle, which aids in shoulder movement and posture. These muscles are essential for everyday activities such as turning the head, maintaining proper posture, and engaging in physical exercise.
Within the cranial part of the accessory nerve, the fibers originate from the nucleus ambiguus, located in the medulla oblongata of the brainstem. These fibers then exit the skull through the jugular foramen, joining the spinal part of the accessory nerve. The spinal part arises from the upper spinal cord, specifically the ventral horn of the cervical spinal segments.
As the accessory nerve traverses through the neck, it intertwines with other vital structures such as the internal jugular vein and the vagus nerve. This intricate arrangement highlights the interconnectedness and complexity of the human body.
Function of the Accessory Nerve
The accessory nerve works in coordination with other nerves and muscles to ensure smooth movement and proper functioning of the head, neck, and shoulders. It plays a significant role in various activities such as speaking, swallowing, turning the head, and shrugging the shoulders.
When you turn your head to look over your shoulder, the accessory nerve is responsible for activating the sternocleidomastoid muscle on the opposite side, allowing for smooth and controlled movement. Similarly, when you shrug your shoulders, the trapezius muscle is activated by the accessory nerve, enabling the upward movement of the shoulders.
Testing the accessory nerve helps in assessing its health and identifying potential abnormalities or damage. Healthcare professionals can perform various diagnostic procedures, such as electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction studies, to evaluate the functionality of the accessory nerve. These tests provide valuable insights into the integrity and performance of this crucial motor nerve.
In conclusion, the accessory nerve is a vital component of the human nervous system, enabling precise control and coordination of head, neck, and shoulder movements. Its complex anatomy and function highlight the remarkable intricacies of the human body. Understanding the accessory nerve not only enhances our knowledge of the human anatomy but also aids in diagnosing and treating potential disorders or injuries affecting this crucial motor nerve.
Preparing for the Accessory Nerve Test
Prior to undergoing the accessory nerve test, several important considerations need to be addressed. This includes gathering necessary equipment and ensuring proper patient preparation.
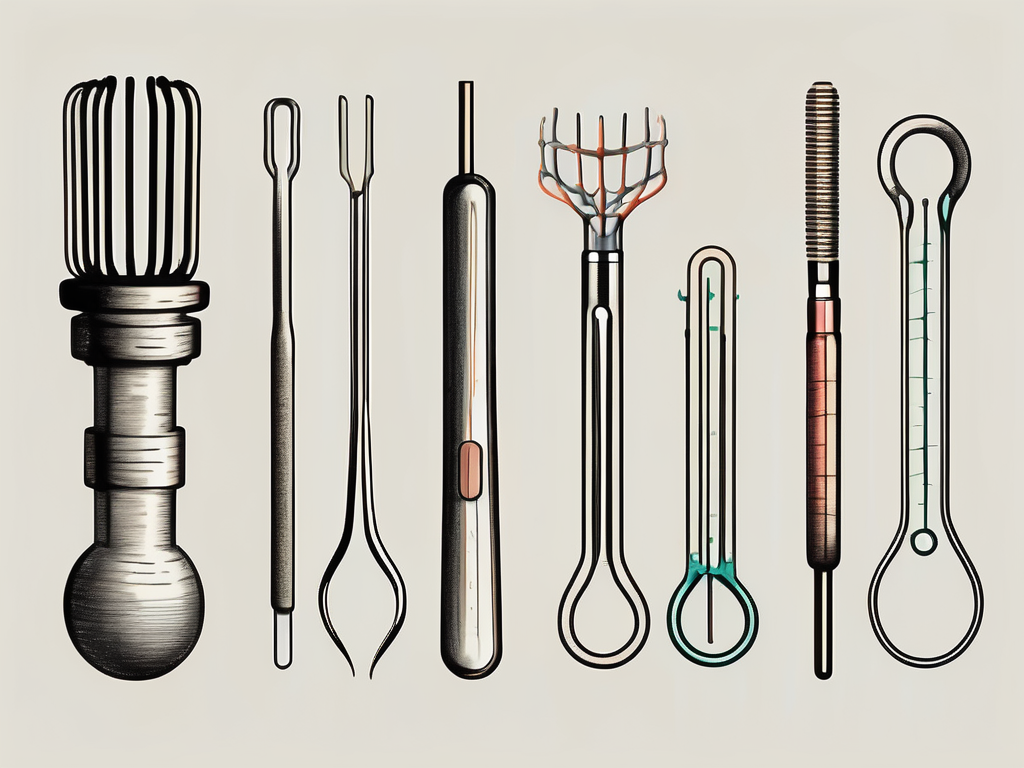
When it comes to assessing the functionality of the accessory nerve, healthcare professionals rely on a variety of specialized equipment. These tools help in accurately conducting the test and recording the electrical impulses produced by the muscles. Among the necessary equipment are electrodes, which are used to detect and measure the electrical activity of the nerve. Additionally, a nerve stimulator is utilized to stimulate the nerve and elicit a response. This response is then recorded using electromyography (EMG) devices, which provide valuable information about the nerve’s functionality.
However, it’s not just the equipment that plays a crucial role in the success of the accessory nerve test. Patient preparation is equally important to ensure accurate results. Before the test, patients are advised to inform their healthcare provider about any medical conditions, allergies, or medications they are currently taking. This information is vital as certain medications can interfere with the accuracy of the test results. By disclosing this information, healthcare professionals can make necessary adjustments to ensure the reliability of the test.
Furthermore, healthcare professionals may provide specific instructions to patients prior to the test. These instructions may include avoiding caffeine or fasting for a certain period of time. Caffeine, for example, can affect the nervous system and potentially alter the test results. Fasting, on the other hand, may be required to ensure accurate measurements of the nerve’s functionality without any external factors influencing the results.
Overall, the accessory nerve test requires both the proper equipment and patient preparation to yield reliable and informative results. By utilizing specialized tools and following specific guidelines, healthcare professionals can effectively assess the functionality of the accessory nerve and provide appropriate medical care based on the test outcomes.
Conducting the Accessory Nerve Test
The accessory nerve test is a crucial diagnostic procedure that evaluates the functionality of the accessory nerve and checks for any abnormalities. This test is performed by healthcare professionals who specialize in neurology or physical medicine and rehabilitation. It involves a step-by-step procedure that requires proper safety measures to minimize discomfort and ensure accurate results.
Step-by-Step Procedure
During the accessory nerve test, the healthcare professional will first explain the procedure to the patient in detail, ensuring that they understand what to expect. This step is essential to address any questions or concerns the patient may have and to establish a sense of trust and comfort.
Once the patient is fully informed and ready to proceed, the healthcare professional will position them in a comfortable manner. This may involve lying down or sitting upright, depending on the specific requirements of the test.
The next step involves attaching electrodes to specific areas such as the neck and shoulder muscles. These electrodes are connected to a nerve stimulator and an electromyography (EMG) device. The nerve stimulator is used to send small electric impulses to the accessory nerve, while the EMG device records the corresponding muscular response.
As the test begins, the healthcare provider will carefully observe and document the results. They will pay close attention to the patient’s muscular response to the electric impulses, looking for any signs of abnormality or dysfunction. This meticulous observation ensures that accurate data is collected for further analysis.
Safety Measures During the Test
Throughout the accessory nerve test, patient safety is of utmost importance. The healthcare professional will take several precautions to ensure a safe and comfortable testing environment.
First and foremost, the healthcare professional will ensure that all equipment used during the test is clean and well-maintained. This includes the electrodes, nerve stimulator, and EMG device. By maintaining proper hygiene and regularly inspecting the equipment, the risk of infection or malfunction is minimized.
Additionally, the healthcare professional will closely monitor the patient’s comfort level throughout the test. They will regularly check in with the patient, asking about any discomfort or pain they may be experiencing. If at any point the patient reports severe pain or any concerning symptoms, the test can be halted immediately to prevent any further discomfort or potential complications.
Furthermore, the healthcare professional will be prepared to handle any adverse reactions or complications that may arise during the test. They will have emergency protocols in place and be trained in basic life support techniques to ensure the patient’s safety and well-being.
In conclusion, the accessory nerve test is a comprehensive procedure that requires careful attention to detail and adherence to safety measures. By following the step-by-step procedure and prioritizing patient safety, healthcare professionals can accurately evaluate the functionality of the accessory nerve and provide valuable insights for diagnosis and treatment planning.
Interpreting the Results of the Accessory Nerve Test
Once the accessory nerve test is complete, the healthcare professional will carefully analyze the results to determine if they are within the normal range or indicate any abnormalities. This interpretation is crucial in developing an accurate diagnosis and planning subsequent treatment.
During the analysis of the results, the healthcare professional will take into consideration various factors. One important factor is the alignment of the electrical impulses produced by the muscles with the nerve stimulation. In a normal accessory nerve test, these impulses should align, indicating that the nerve is functioning correctly. This alignment is a positive sign and suggests that there are no significant abnormalities.
However, in the case of abnormal findings, such as reduced or absent muscular response, it may suggest nerve dysfunction, injury, or certain medical conditions that require further investigation and evaluation. These abnormal findings can provide valuable insights into the underlying cause of the patient’s symptoms and help guide the healthcare professional in developing an appropriate treatment plan.
Normal vs. Abnormal Findings
Normal findings in the accessory nerve test provide reassurance that the nerve is functioning properly. This can be a relief for both the patient and the healthcare professional, as it eliminates the need for further invasive tests or interventions. It also allows the healthcare professional to focus on other potential causes of the patient’s symptoms.
On the other hand, abnormal findings can raise concerns and warrant further investigation. The healthcare professional may consider additional tests, such as imaging studies or nerve conduction studies, to gather more information about the extent and nature of the nerve dysfunction. These additional tests can help confirm the initial findings and provide a more comprehensive understanding of the patient’s condition.
Potential Complications and Their Indications
While the accessory nerve test is generally considered safe, there are potential complications that could arise. It is important for both the healthcare professional and the patient to be aware of these complications and their indications.
One potential complication is temporary discomfort at the electrode insertion site. This discomfort is usually mild and resolves on its own within a short period of time. It is important for the patient to communicate any significant or persistent discomfort to the healthcare professional, as it could indicate a need for further evaluation.
Bleeding at the electrode insertion site is another potential complication. This bleeding is typically minimal and stops on its own. However, if the bleeding is excessive or persists, it is important to seek immediate medical attention. Excessive bleeding could indicate an underlying issue that needs to be addressed.
Infection is a rare but possible complication of the accessory nerve test. Signs of infection include redness, swelling, warmth, and increased pain at the electrode insertion site. If a patient experiences any of these symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional immediately. Prompt treatment can help prevent the spread of infection and ensure proper healing.
Overall, the interpretation of the results of the accessory nerve test plays a crucial role in the diagnostic process. It provides valuable information about the functioning of the nerve and helps guide the healthcare professional in developing an appropriate treatment plan. By understanding the normal and abnormal findings, as well as the potential complications, both the healthcare professional and the patient can work together to ensure the best possible outcome.
After the Accessory Nerve Test
After the completion of the accessory nerve test, certain post-test care and recommendations should be followed to ensure a smooth recovery and accurate assessment of the results.
During the test, electrodes are placed on the skin over the accessory nerve, which is located in the neck. The nerve is then stimulated with a mild electrical current, and the response is recorded. This test helps to evaluate the function of the accessory nerve and identify any abnormalities.
Once the test is complete, patients may experience some mild discomfort or temporary numbness in the area where the electrodes were placed. This is normal and should resolve within a few hours. It is important to avoid touching or scratching the area to prevent any irritation or infection.
Post-Test Care and Recommendations
Patients are typically advised to avoid strenuous activities or heavy lifting for a short period following the test. This is to allow the body to recover and minimize the risk of any complications. It is essential to carefully follow any specific instructions provided by the healthcare professional regarding post-test care.
In addition to physical rest, it is also important to take care of your mental well-being. The accessory nerve test can sometimes be an anxiety-inducing experience, and it is normal to feel a range of emotions afterward. Engaging in relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises or meditation, can help promote a sense of calm and reduce any lingering stress or anxiety.
If any symptoms or concerns arise after the test, it is advisable to promptly consult with a healthcare provider. While it is common to experience some mild discomfort or temporary numbness, persistent or worsening symptoms should be evaluated by a medical professional. They can assess the situation and provide appropriate guidance or treatment if necessary.
When to Schedule a Follow-up Test
In certain cases, additional tests such as imaging studies or further evaluations may be recommended based on the results of the accessory nerve test. The need for a follow-up test is determined by the healthcare professional, who will assess the patient’s individual circumstances and medical history to ensure appropriate care.
Follow-up tests may be necessary if the accessory nerve test reveals any abnormalities or if the results are inconclusive. These additional tests can provide more detailed information about the condition of the accessory nerve and help guide further treatment decisions.
It is important to communicate openly with your healthcare provider and ask any questions you may have about the need for a follow-up test. They can explain the reasons behind the recommendation and address any concerns or uncertainties you may have.
Remember, the accessory nerve test is just one part of the diagnostic process. It is a valuable tool in assessing the function of the accessory nerve, but it is not the sole determinant of a diagnosis. Your healthcare provider will consider the test results in conjunction with your medical history, physical examination, and other relevant factors to form a comprehensive assessment of your condition.
Frequently Asked Questions about Accessory Nerve Test
There are several common concerns and misconceptions regarding the accessory nerve test. Let’s address a few of them:
Common Concerns and Misconceptions
- Is the accessory nerve test painful?
- Can the test diagnose all accessory nerve-related conditions?
- Are there any risks associated with the test?
It is important to discuss these concerns with a healthcare professional as they can provide accurate information tailored to an individual’s specific situation.
Tips for a Smooth Testing Experience
- Follow all instructions provided by the healthcare professional
- Arrive at the test well-rested and relaxed
- Be honest about any allergies, medications, or medical conditions
- Communicate any discomfort or concerns during the test
By adhering to these tips, patients can have a more comfortable and successful accessory nerve testing experience.
Overall, understanding the process of testing the accessory nerve is crucial in diagnosing and managing various neurological conditions. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for accurate evaluation, interpretation of test results, and to develop an individualized treatment plan based on specific circumstances. By doing so, patients can receive the best possible care and improve their overall quality of life.