how to assess accessory nerve
In this article, we will explore the process of assessing the accessory nerve and understanding its anatomy, function, and potential disorders. By following the necessary steps and precautions, healthcare professionals can ensure accurate assessment results and provide appropriate patient education and management. Remember, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider for individualized guidance and diagnosis.
Understanding the Accessory Nerve
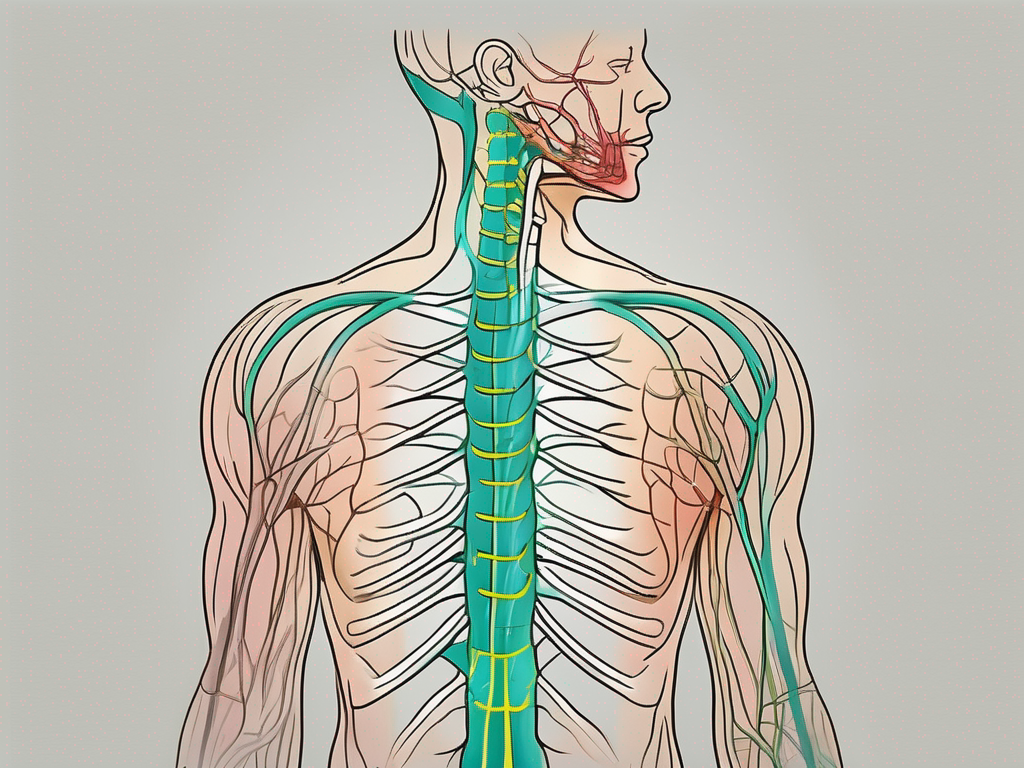
The accessory nerve, also known as cranial nerve XI, is a motor nerve that originates from the brainstem. It consists of two main components: the cranial portion and the spinal portion.
The cranial portion arises from the nucleus ambiguus, a cluster of neurons located in the medulla oblongata. This portion of the nerve is responsible for controlling the muscles involved in swallowing and phonation. It plays a crucial role in coordinating the movements of the soft palate, pharynx, and larynx during speech and swallowing.
The spinal portion of the accessory nerve emerges from the upper cervical spinal cord segments. It then travels through the jugular foramen, a bony opening located at the base of the skull, and joins the cranial portion. This union of the two portions results in the innervation of specific muscles involved in head and neck movements.
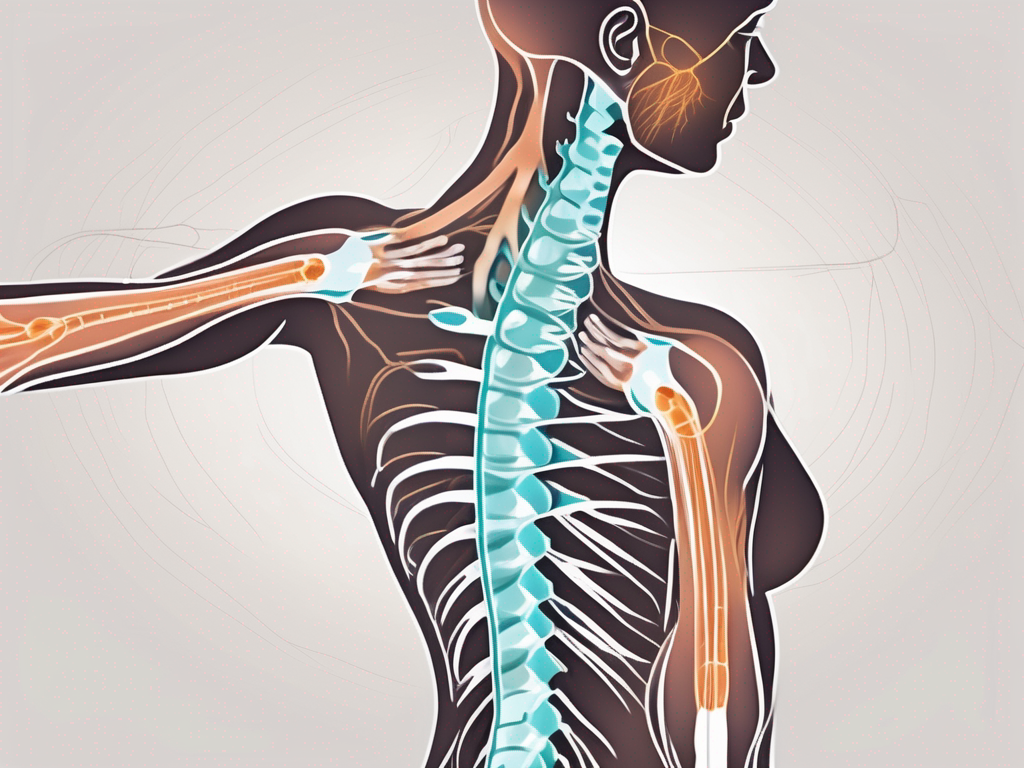
The accessory nerve primarily supplies motor innervation to two muscles: the sternocleidomastoid and the trapezius.
The sternocleidomastoid muscle, also known as SCM, is a large muscle located on each side of the neck. It originates from the sternum and clavicle and inserts into the mastoid process of the temporal bone. The SCM muscle facilitates head rotation, allowing us to turn our heads from side to side.
The trapezius muscle is a broad, flat muscle that extends from the base of the skull and upper spine to the shoulder blades and the middle of the back. It is responsible for various movements, such as shrugging the shoulders, retracting the scapulae (pulling the shoulder blades back), and rotating the scapulae. The trapezius muscle plays a crucial role in maintaining proper posture and stabilizing the shoulder girdle.
Assessing the accessory nerve’s functioning can help identify any abnormalities that may affect a patient’s range of motion and quality of life. Dysfunction of the accessory nerve can result in weakness or paralysis of the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles, leading to difficulties in head and neck movements. Physical therapists and healthcare professionals often perform specific tests to evaluate the strength and coordination of these muscles, helping to diagnose and treat any issues related to the accessory nerve.
Preparing for the Assessment
When it comes to conducting an assessment, proper preparation is key. This not only ensures accurate results but also promotes a positive experience for the patient. In this section, we will discuss the necessary equipment and patient preparation guidelines to follow before conducting an assessment.
Necessary Equipment for Assessment
Before diving into the assessment, it is important to gather all the essential equipment. Here are a few items that should be readily available:
- Disposable gloves: Maintaining hygiene is crucial in any healthcare setting. Disposable gloves not only protect the healthcare professional from potential contaminants but also ensure the patient’s safety.
- Measuring tape: To accurately document muscle strength and range of motion, a measuring tape is a must-have. This tool allows for precise measurements and helps in tracking any changes over time.
- Penlight: When examining the patient’s neck and shoulder area, a penlight can be incredibly useful. It provides a focused beam of light, allowing for a detailed examination of these specific regions.
Patient Preparation Guidelines
Preparing the patient for the assessment is just as important as gathering the necessary equipment. By following these guidelines, you can ensure that the patient is comfortable and ready for the assessment:
- Explain the procedure: Taking the time to explain the assessment procedure and its purpose to the patient is essential. This helps alleviate any concerns or anxieties they may have, allowing them to feel more at ease throughout the process.
- Choose appropriate clothing: Request that the patient wears loose-fitting clothing that provides easy access to the neck and shoulder areas. This ensures that the healthcare professional can perform the assessment without any restrictions.
- Create a comfortable environment: A comfortable and well-lit examination environment is crucial for both the patient and the healthcare professional. This helps promote relaxation and enhances the accuracy of the assessment results.
By following these guidelines and ensuring that you have all the necessary equipment, you are well-prepared to conduct a thorough assessment. Remember, proper preparation sets the stage for a successful evaluation and ultimately leads to effective patient care.
Conducting the Accessory Nerve Examination
The examination of the accessory nerve is an important part of assessing the strength and functionality of the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles. This examination involves a series of physical maneuvers that allow healthcare professionals to evaluate the patient’s muscle strength and movement.
Physical Examination Techniques
When conducting the accessory nerve examination, there are specific techniques that healthcare professionals follow:
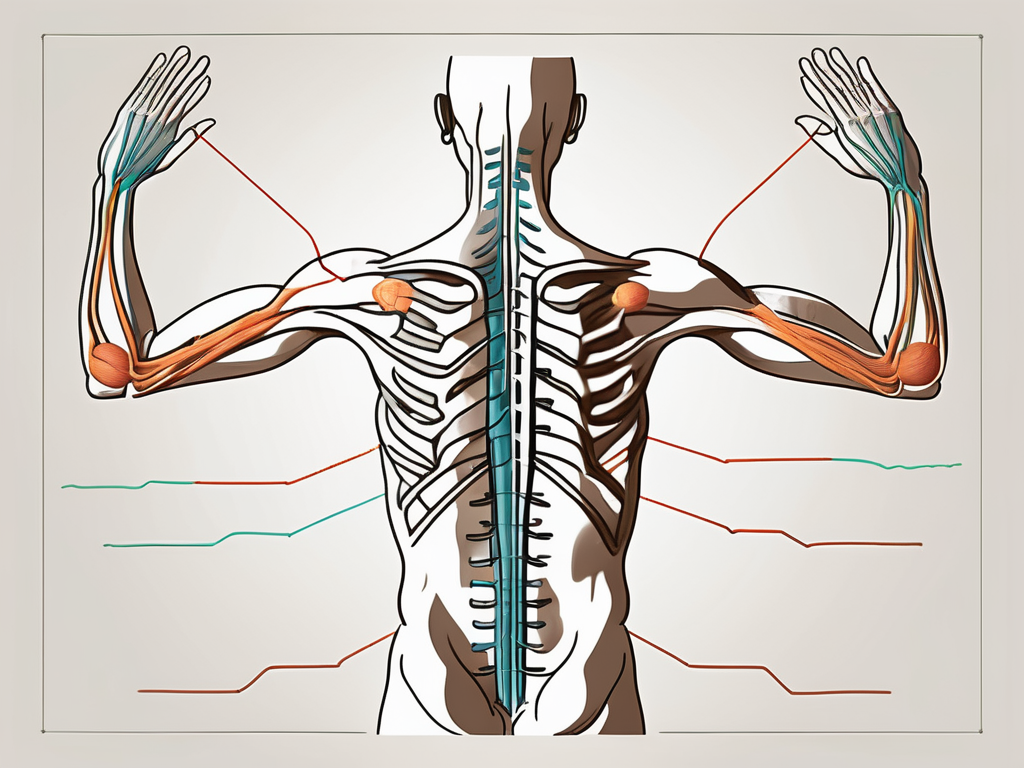
- Assessing the sternocleidomastoid muscle: The examiner instructs the patient to rotate their head to each side against resistance. This maneuver helps evaluate the strength and symmetric contraction of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. As the patient performs the movement, the examiner palpates the muscle to assess its strength and any abnormalities.
- Evaluating the trapezius muscle: The examiner observes the patient’s ability to perform shoulder shrugging and scapular retraction against resistance. These movements help assess the strength and symmetry of the trapezius muscle. By applying resistance, the examiner can determine if there are any weaknesses or limitations in the muscle’s functionality.
These physical examination techniques provide valuable information about the patient’s muscle strength and movement capabilities. By assessing the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles, healthcare professionals can identify any abnormalities or asymmetries that may indicate underlying conditions or injuries.
Observing Muscle Strength and Movement
During the accessory nerve examination, healthcare professionals pay close attention to the patient’s muscle strength and movement. By carefully observing these aspects, they can gather important information for further analysis and diagnosis.
Abnormalities in muscle strength, such as weakness or limited range of motion, can indicate various conditions affecting the accessory nerve or the associated muscles. These conditions may include nerve damage, muscle disorders, or injuries. By documenting these findings, healthcare professionals can track changes over time and monitor the effectiveness of any treatment plans.
Additionally, assessing the symmetry of muscle contraction and movement is crucial during the examination. Any noticeable differences between the two sides of the body may suggest underlying issues that require further investigation.
In conclusion, the accessory nerve examination is a vital component of assessing the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles. By utilizing specific physical examination techniques and closely observing muscle strength and movement, healthcare professionals can gather valuable information to aid in diagnosis and treatment planning.
Interpreting the Assessment Results
When it comes to interpreting the assessment results for the accessory nerve, it is essential to have a comprehensive understanding of what constitutes normal versus abnormal findings. This understanding allows healthcare professionals to identify any potential issues with the nerve’s functioning.
One of the key aspects to look out for during the assessment is any asymmetry in the findings. If there is a noticeable difference between the two sides of the body, it could indicate a problem with the accessory nerve. Additionally, any weakness or restricted muscular movements observed during the assessment should also raise concerns.
However, it is important to note that abnormal findings alone are not enough to make a definitive diagnosis. To accurately assess the situation, healthcare professionals must consider the patient’s medical history and other diagnostic test outcomes. This comprehensive approach helps in identifying potential disorders related to the accessory nerve.
Potential Disorders of the Accessory Nerve
There are several conditions that can affect the normal functioning of the accessory nerve. One such condition is nerve damage, which can occur due to trauma, injury, or certain medical conditions. Nerve damage can disrupt the communication between the brain and the muscles, leading to various symptoms.
Tumors can also pose a threat to the accessory nerve’s functioning. When a tumor develops near or on the nerve, it can exert pressure and cause compression. This compression can result in pain, muscle weakness, and limited mobility.
Furthermore, other factors such as inflammation or infections can also affect the accessory nerve’s performance. Inflammation can irritate the nerve, leading to discomfort and dysfunction. Infections, on the other hand, can directly target the nerve and cause damage.
When abnormal findings are present during the assessment, healthcare professionals should consider further investigations and consultations with specialists. These additional steps are crucial in determining and managing the underlying cause of the abnormal findings. By working closely with experts in neurology and other related fields, healthcare professionals can develop a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to the patient’s specific needs.
Follow-up Procedures after Assessment
After an accessory nerve assessment, it is crucial for healthcare professionals to follow certain procedures to ensure the best possible care for their patients. One important step is the referral process for abnormal findings.
Referral Procedures for Abnormal Findings
When abnormal findings are detected during the accessory nerve assessment, healthcare professionals should promptly refer the patient to appropriate specialists, such as neurologists or orthopedic surgeons. These specialists have the expertise to further investigate the abnormal findings, conduct confirmatory tests, and develop personalized treatment plans.
Referrals are essential to ensure that patients receive the specialized care they need. By involving specialists, healthcare professionals can ensure that the patient’s condition is thoroughly evaluated and that the most appropriate treatment options are explored.
Collaboration between healthcare professionals and specialists is key in providing comprehensive care and improving patient outcomes. Through referrals, patients can benefit from the collective knowledge and expertise of a multidisciplinary team.
Patient Education and Management
In addition to referrals, healthcare professionals also play a vital role in educating patients about their condition and providing management strategies for improved quality of life.
Depending on the underlying disorder detected during the accessory nerve assessment, treatment options may vary. It is important for healthcare professionals to discuss these options with patients, taking into consideration their specific needs and preferences.
One common treatment option for accessory nerve disorders is physical therapy. Physical therapists can work with patients to develop customized exercise programs that help improve strength, flexibility, and overall function of the affected muscles.
In some cases, medication may be prescribed to manage symptoms or address underlying causes of the abnormal findings. Healthcare professionals can explain the benefits and potential side effects of these medications, ensuring that patients are well-informed and able to make informed decisions about their treatment.
In more severe cases, surgery may be necessary to correct or alleviate the underlying issue affecting the accessory nerve. Healthcare professionals can discuss the surgical options, risks, and expected outcomes with patients, helping them make informed decisions about their care.
It is crucial for healthcare professionals to emphasize the importance of following their recommendations and seeking ongoing support. By adhering to the prescribed treatment plan and seeking regular follow-up care, patients can maximize the effectiveness of their management strategies and promote their recovery.
Furthermore, healthcare professionals can provide information about support groups or resources that can offer additional assistance and guidance. These resources can provide patients with a sense of community and understanding, helping them navigate their condition more effectively.
In conclusion, the follow-up procedures after an accessory nerve assessment involve referral processes for abnormal findings and patient education and management. By promptly referring patients to specialists and providing comprehensive education and management strategies, healthcare professionals can ensure that patients receive the best possible care and support for their condition.
Safety Measures and Precautions
Risks Associated with Accessory Nerve Assessment
While accessory nerve assessment is generally safe, some risks and potential complications may arise. These include discomfort during the examination, temporary muscle soreness, or rare instances of nerve injury.
It is important for healthcare professionals to be aware of these risks and take necessary precautions to ensure patient safety. By following established protocols and guidelines, healthcare providers can minimize the occurrence of adverse events and promote a safe assessment process.
During the assessment, healthcare professionals should carefully monitor the patient’s response and communicate openly to address any discomfort or concerns. By maintaining a high level of attentiveness and responsiveness, healthcare providers can help alleviate any potential risks and ensure a positive patient experience.
In rare cases where a nerve injury occurs, it is crucial for healthcare professionals to promptly recognize and manage the situation. This may involve consulting with specialists, implementing appropriate treatment strategies, and providing necessary support to the patient throughout the recovery process.
Ensuring Patient Comfort and Safety
Prioritize patient comfort and safety throughout the assessment process. Be attentive to their needs, concerns, and pain tolerance. Each patient is unique, and healthcare professionals should adapt their approach accordingly to ensure a comfortable and safe experience.
Creating a supportive environment is essential in promoting patient well-being. Healthcare professionals should take the time to explain each step of the assessment, providing clear instructions and addressing any questions or anxieties patients may have. By fostering open communication, patients can feel more at ease and confident in the assessment process.
Additionally, healthcare providers should consider implementing strategies to minimize discomfort during the examination. This may include using appropriate positioning techniques, providing cushions or supports to enhance patient comfort, and utilizing local anesthesia when necessary.
By following these safety measures and precautions, healthcare professionals can perform the accessory nerve assessment accurately and contribute to patients’ overall well-being. It is important to remember that patient safety should always be the top priority in any medical procedure.
Remember, this article provides an overview of how to assess the accessory nerve. Consult with a healthcare provider for personalized guidance, diagnosis, and appropriate treatment options.