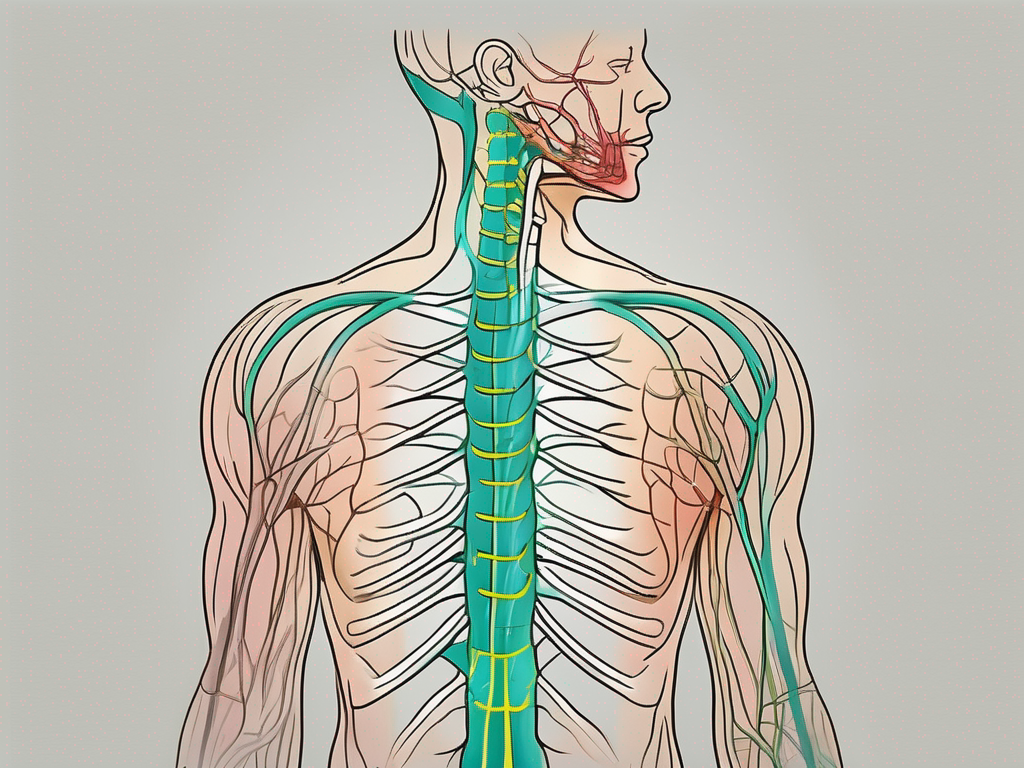
what part of cervical plexus is the psinal accessory nerve from
Discover the intricate connection between the spinal accessory nerve and the cervical plexus in this insightful article.
what fingers do the spinal accessory nerve control
Discover the fascinating role of the spinal accessory nerve in controlling specific muscles in the body.
what is cranial accessory nerve
Discover the ins and outs of the cranial accessory nerve in this comprehensive article.
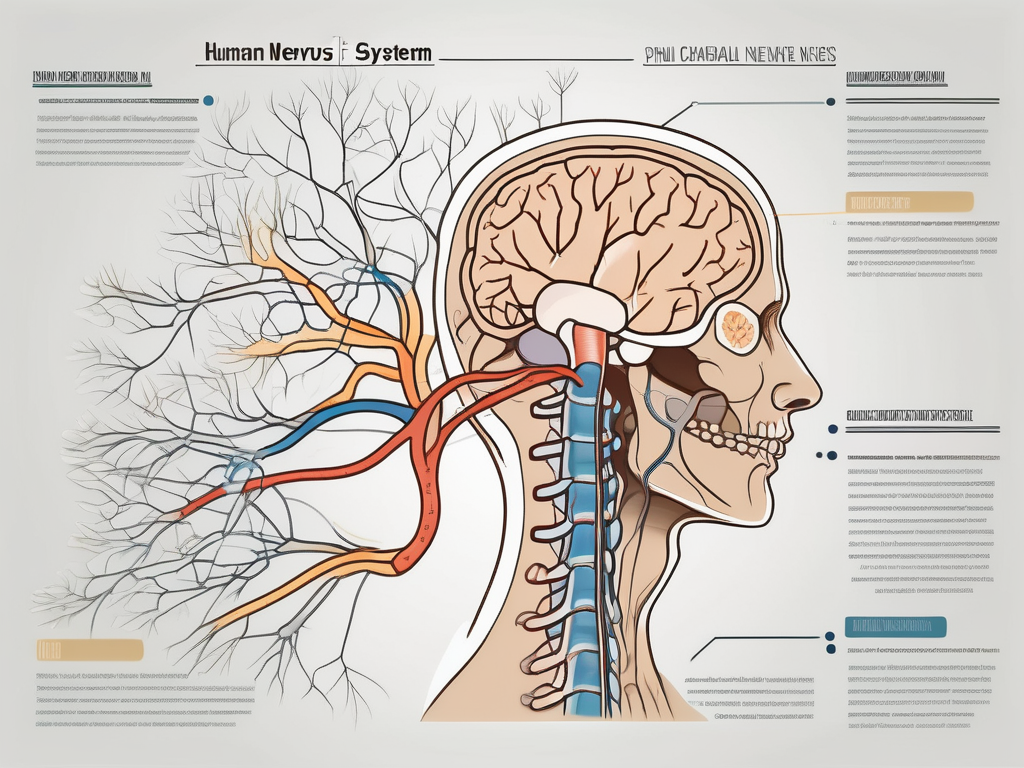
why is the spinal accessory nerve not a true cranial nerve
Explore the fascinating intricacies of the spinal accessory nerve and its classification as a cranial nerve.
what number is the spinal accessory nerve
Uncover the mystery behind the spinal accessory nerve and its numerical identity in this fascinating article.
what signal does the accessory nerve motor sensory
Discover the fascinating role of the accessory nerve in both motor and sensory functions.
what symptoms would you associate with damage to the spinal accessory nerve
Discover the telltale signs of spinal accessory nerve damage in this comprehensive article.
spinal accessory nerve supplies what musccles
Discover the intricate connection between the spinal accessory nerve and the muscles it supplies in this insightful article.
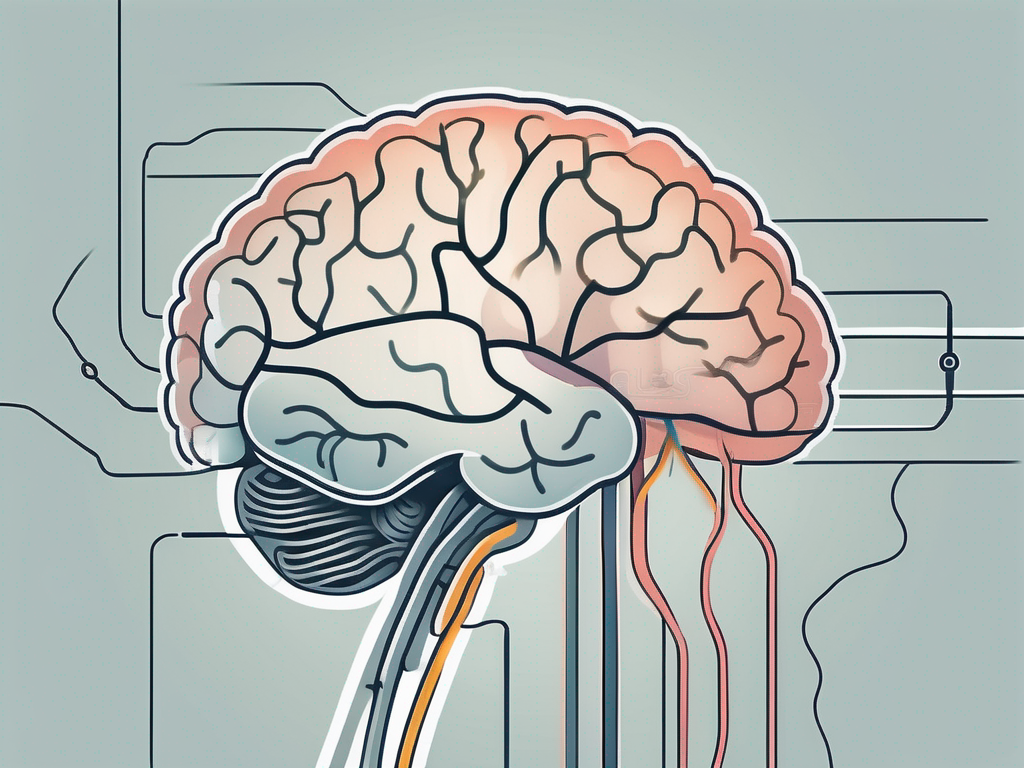
where does the accessory nerve leave the brain
Explore the fascinating journey of the accessory nerve as it departs the brain, and delve into the intricate pathways it traverses.
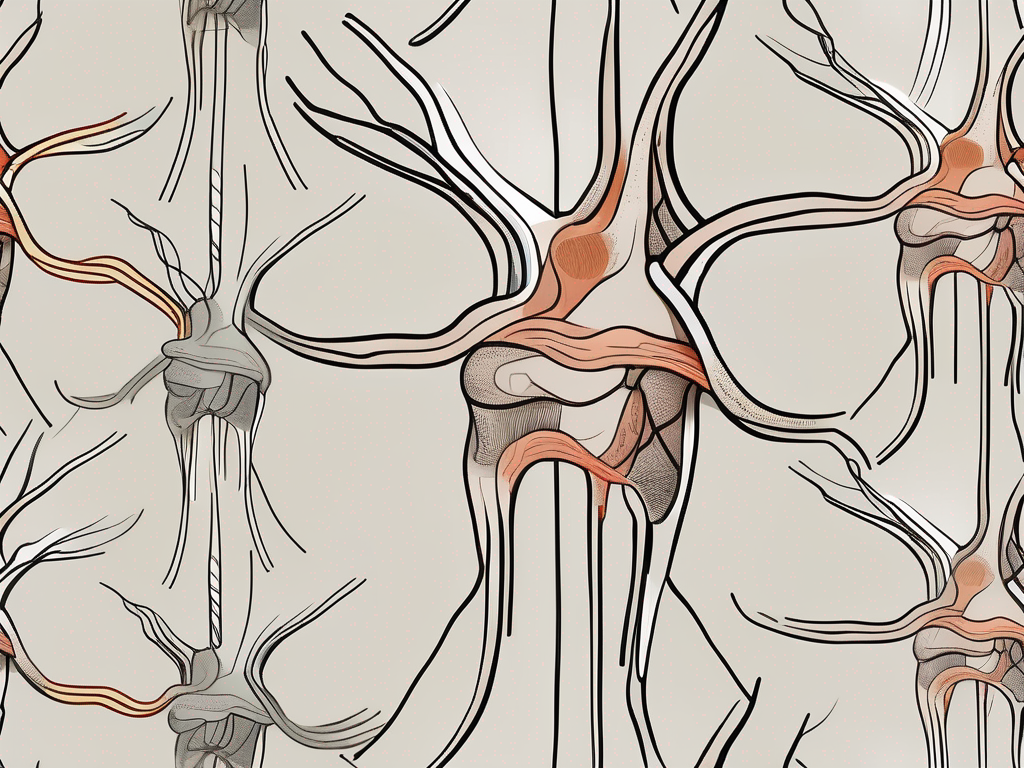
how many roots does the accessory nerve have
Uncover the mystery of the accessory nerve as this article delves into the intriguing question of how many roots it truly possesses.